Preserving and caring for records of enduring value means that the legacy of a person or community is kept for future generations. This is the mission of our archives. We hope this short video captures this.
research
Researching your heritage home in Ontario
By Noelle Tangredi
There are many reasons to like old houses–the architecture, the decorative details and high ceilings. but many old home lovers feel a connection to the history of their old home. Every house has its story. Wouldn’t it be great to uncover those stories and learn about the families that lived there before you? It’s not that difficult to do—and believe me, it can become a little addicting!
Things you can often find out about your old home include: the year it was built, the first owners and or tenants, the original purchase price or historical assessments, information about historic land transactions and subdivision plans. You can also piece together stories of families that lived there and what their lives were like, if any of them went to war, what kind of jobs they may have had, when they were born, married and died and more. Nothing is a sure thing and sometimes information is limited, difficult to find or interpret, but once you find something, it’s hard not to keep going. Below are some tips on how and where to start.
Start with determining the build date
Check with your local architectural preservation society about your house first and see if there’s any information written on it already. If it’s a designated heritage home, there may be a report written on it. If you are interested in the architecture of your home, a good primer on architecture styles in Ontario can be found at this link: Index Page – Ontario Architecture.
The age of your house can be determined pretty closely by using several different resources:
Researching the building
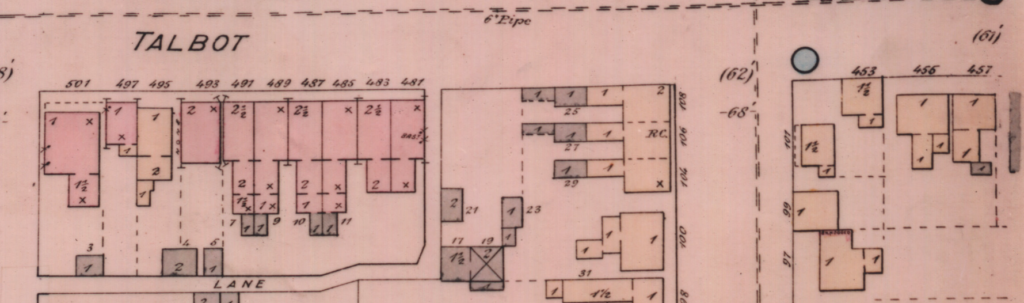
Fire Insurance Plans
These are hand drawn maps that show what buildings were on a particular lot according to the date it was last revised. It provides a visual footprint of the building, what materials it was made from and if there are any outbuildings. These very helpful to pinpoint a timeframe for your house’s construction and even if there might have been another house on the lot that was replaced by the current one. The map provides clues to changes in the structure or house number or even street name changes over the years. These maps are often kept in City or County Archives or Libraries and are sometimes available online.
City Directories
All cities had a directory that functioned as a phone book before there were telephones (and even afterwards). They have two sections. One is organized by street address (street names in alphabetical order, separated by odd and even numbers with cross streets shown). This section will show the name of the head of the household at each address. If you have an idea of when your house might have been built, start with that. If you find it, keep working backwards until you do. This will be the year it was finished and occupied. The previous year will likely be a more accurate build date based on when the information was gathered for the directory and when it was published. If you don’t find your address, keep going ahead until you do. Sometimes you’ll find it listed as “unfinished house” or “new”.
The second part of the directory is alphabetical by last name. Use this to find out the occupation of the head of the household and sometimes others living at the same residence (a wife’s name, for example). If the directory names the householder’s place of business, you can also consult the directory for more information on what kind of work was done there, the address and even sometimes an advertisement.
Directories are usually the easiest way to pin down information on your home’s history. These are usually located either in their original format or on microfiche in your local library or city and county archives. Some are even located online.
Tax assessment rolls, Registered Plans and Property Transactions
Although a little more complicated to get a hold of and understand, these documents can give you very interesting information about who built your house, when and for how much. What the land was assessed at for tax purposes over the years and even strange details like how many dogs, chickens or horses were on the property when it was assessed! It can also answer questions about whether the first occupants of the house were owners or tenants. These records could be located in your local city or county archives or possibly through your city hall.
Researching Occupants’ Lives
Canadian Censuses
Once you know the year of construction and the names of early occupants and possible occupations, you can start pulling out the stories of their lives. A good place to start is the censuses for your area. Library and Archives Canada has a searchable database here: Censuses – Library and Archives Canada. If you don’t come up with your people right away, try various family members and different years. Sometimes transcription or spelling errors happen in digitization. The census will reveal all of the people living in the house when the census taker visited the home. This is a good way to find out children’s names and the birthdates of family members to help with further research. You may also discover that others lived in the home, such as lodgers, other relatives or servants. Ancestry.ca also has census records and if you can’t find your people on the LAC site, you might have luck there.
Ancestry.ca
Armed with what you learned from the census will help you more accurately search in genealogy services such as: Ancestry.ca. Here you can find out birth, death and marriage dates and sometimes school info, photos and family trees. These details will help pull together various bits of information into stories, such as the lives of new immigrants, the birth of family businesses and the tragedies of early deaths due to local epidemics, war or accidents. Ancestry.ca is usually available for free through your local library.
Military Records
If you suspect that an occupant of your house may have served during wartime, you can search for and read personnel files on the Library and Archives Canada website. Ancestry.ca may have some documents but the LAC website has the complete files:
Library and Archives Canada.

Local Newspaper Articles
Your local library or archives may have local newspaper articles available but likely not searchable. The website Canadiana.ca houses many digital documents and has a section with local magazines and newspapers. I’ve found that newspaper articles from “back in the day” usually include a lot of personal information, including home addresses. If you search these papers for you address, you may find some pretty interesting stories! Visit: Serials: Periodicals, Annuals and Newspapers – Canadiana.

These are just a few places for you to start. Local librarians, archivists and historians will be able to point you in the direction of more information. Happy researching!
What do you know about your ancestors?
By Colleen Callahan Gilbert
Recently there has been an explosion of interest in the field of family history research (otherwise known as genealogy). One reason could be the uncertainty of tomorrow’s future, economically and metaphysically. We are not alone in these unsettling times. Throughout history, our ancestors encountered great depressions and extreme poverty worse than we can imagine. The events and patterns of our present day take on a new appreciation for our family’s past. For some, the study of your family’s history can bring about a feeling of stability in our ever-changing world. For others, genealogy is looked upon as an adventure. It is exciting and challenging. Regardless of whatever piqued your interest in your past, now is the time to take advantage of all the wonderful genealogical resources we have at our disposal.

Where to begin? A good place would be in your own home where you will find evidence of your family history all around you. Begin with yourself. Start by writing down your full name, and then your father’s and mother’s full names working as far back as you are able. Always work from the known to the unknown. Remember to base your calculations on facts, which in turn will help resolve the unknown. Complete as much as possible including the vital statistics of you and your parents. You now have two generations. Now may be a good time to begin charting your new family information. Two simple genealogical charts: the pedigree chart and the family group chart could be used to start putting your genealogy into perspective. Blank charts can be found for free on Cyndi’s List – United States. As your tree expands, you may want to use a genealogical software program to aid in your organization.
Next, check for primary records at home. Primary records are any records created at the time of the event. These would include birth, marriage, and death certificates. Family letters, journals, and diaries could be primary sources if they are recording a particular occasion such as soldier writing home describing his war experiences or a midwife documenting the birth of a child. A death record is a primary source, but also a secondary source for the birth of the deceased. After learning all you can at home, the next step would be contacting and interviewing older relatives who could add not only more pertinent family information, but wonderful stories of the past. With their permission, an audio or video recording would be an excellent way to help document your research. Older relatives’ narratives are a great way to jump start your investigation. They can offer limitless clues for moving backward into new undiscovered territory. But remember—not all stories told are 100% factual. Your Aunt Sally or Grandma Smith may be convinced the family legend is true, but until proven, they are just clues to help you move on.
Bible records are another excellent source of family information. In the past, documenting birth, marriage, and death records were frequently done by writing in the family Bible. Before vital records were required by the county or state, our ancestors often kept their own family records. The value of the Bible records depends greatly on who wrote the records. Was he or she a witness to a birth or death? Or was this secondhand information which was later added to the Bible? Whatever may be the case, Bible records are truly an invaluable research source to the genealogist.
After gleaning as much information from home and family you are probably ready to explore outside sources such as the Internet, library, and the Family History Center. The Internet contains a huge treasure trove of information. Websites such as Ancestry and FamilySearch have literally millions of records at your disposal; in addition, they offer guidance in the way of classes and online seminars. While Ancestry.com is a subscriber-only site, FamilySearch is free to the public. Keep in mind, as you venture into online genealogy that you will not find everything you are seeking to complete your genealogical history. Many records are simply not online. Remember also that just because it is online does not make it true. Many genealogies posted are filled with inaccuracies. You should always do your own research and use the information posted only as a guide.
Most libraries are genealogy friendly. The main headquarters in London, Ontario has a wonderful genealogy area where library patrons can utilize the Internet just for their research. It also subscribes to Ancestry.com for in library use only, although during the pandemic, it is available by logging in from home with your library card. In addition, the library houses an extensive collection of genealogical books and old newspapers.
You’ve been warned: this is a very addicting hobby! Once you begin and find out the real story behind the disappearance of great Uncle Joe or why your great, great grandfather left Ireland in such great hurry, you will be hooked. Like a detective you may travel to archives, county court houses, and cemeteries trying to find that distant cousin who keeps evading you at every turn. If you are seeking only perfect ancestors, then genealogy is probably not for you. Like it or not, there will no doubt be a black sheep or two in your family if you look long enough.
Genealogy is for everyone: young, old, rich or poor. We all have a past which is begging to be discovered. What do you know about your ancestors?
Catholic Research Resources Alliance
A wonderful site for those interested in the history of women religious can be found at Catholic Research Resources Alliance. Here are some of the resources you will find at this website:
- a description of the Catholic portal with a search box and introductory video The Catholic Portal
- the Catholic News Archive The Catholic News Archive
- subject guides LibGuides at Catholic Research Resources Alliance
- bibliographies, directories and reports Bibliographies, Directories, and Reports
Our consolidated archives can be found on this site as well! We encourage you to visit today, if you are interested in researching the history of women religious.
